Many marketers, especially SEOs, see zero-click searches, (searches that do not end up with people clicking on anything in the search results) as problematic.
Searching Google for information about the weather, election results, my dental office’s contact numbers, the answers are right in front of my eyes -meaning that I don’t need to scan through the snippets, click a result, or check through the content to find the answer.
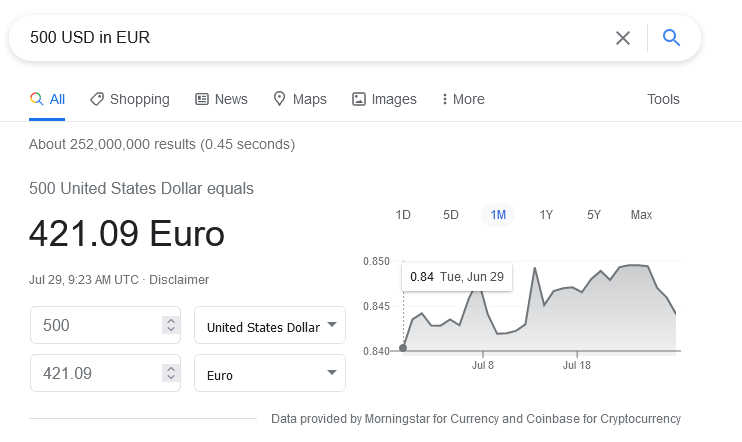
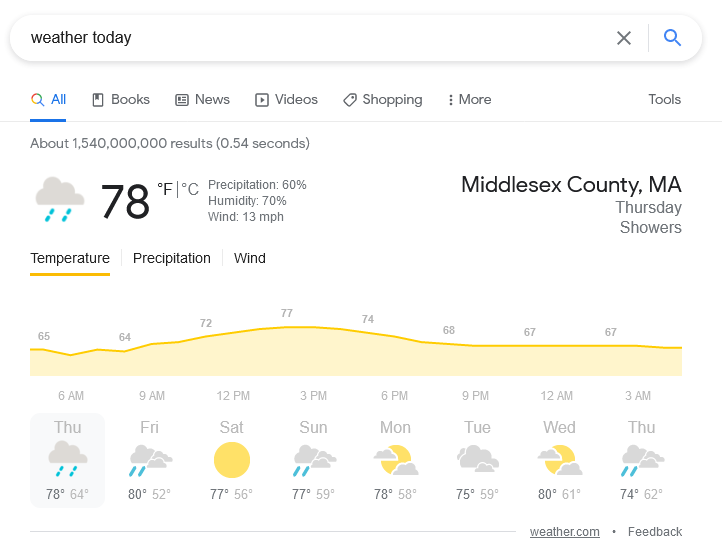
While this is definitely a handy development for users, SEOs are concerned, because SEO is all about getting traffic to the website/webpages from Google or another search engine.
SparkToro, in its recent blog post, said that, when SimilarWeb analyzed 5.1 trillion Google searches in 2020, they found that only 34% of the searches resulted in clicks. But Google contested these findings, saying that its search engine has increased visits to websites every year.
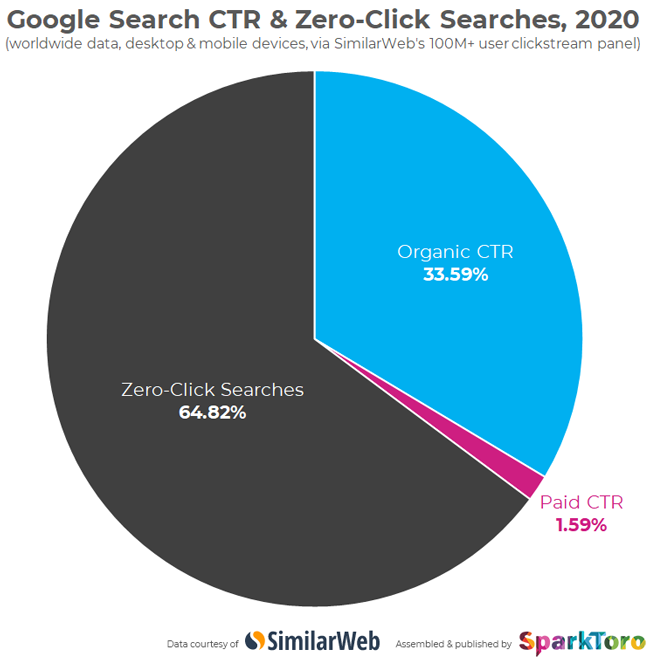
For example, SparkToro said that fewer clicks are going to websites. But Google claims that its search engine has increased visits to websites every year.
Here are some details from the SparkToro study:
Twitter exploded right after this, and relatively several discussions happened. Followed by this, Google released a blog post claiming that the study wasn’t reliable for the following reasons:
All of this suggests that more information is being distributed in relevant zero-click answers.
Where does Google obtain the answers in its SERPs that deliver users the information they need, so they do not need to click further (i.e., the search ends up with zero click-throughs)? The answer is straightforward – website content and content marketing.
Examine the content of your website. Make sure it is relevant, unique, and of editorial quality. Does it answer the critical question of “Why would I choose this business?” Does it address all the crucial questions and concerns of your customer segments? Do you have detailed descriptions of your services and products?
FAQs are components of the website content that have earned importance in the era of mobile search and voice assistants. Prospective customers appreciate the valuable information they can find in FAQs. It allows them to find a quick, well-formulated answer to questions they might have.
Schema markup helps search engines understand websites’ content and intent, especially dynamic content elements such as events and happenings pages, special offers, opening hours, star ratings, FAQs, and videos.
Do you publish blogs/content assets very frequently? Are you running a news portal? Is your business getting a lot of visitors via mobile devices? – If your answers are “YES,” AMP is the feature for you. AMP increases visibility and creates an extra access point to improve mobile visitors and bookings/actions and provide another chance to outperform the competition.
Okay, we have seen enough about what a zero-click search is. How can you leverage it? How can you optimize for zero-click searches?
If you’re trying to optimize for zero-click searches, do traditional SEO KPIs make sense? The answer is a big NO. You will want to modify your SEO KPIs to align with zero-click searches.So, what should SEOs care about? What KPIs to track and monitor while optimizing for zero-click searches?
If you are aiming for a “featured snippet,” your KPI should be tied to impression share.
1. Track search impressions from GSC for the LPs that you optimize for zero-click searches.
2. If you’re into local SEO, the zero-click search behavior can be overwhelming. Here are the three significant segments where the zero-click search can happen:
“You can use call history to keep track of phone calls from your customers on Google Search and Maps. Your needs are all in one place to help you respond to missed calls and stay engaged with your customers.
These calls may make it easier for you to find and do business with customers who found your business through Google. Any calls you get from your Business Profile will start with a short message that lets you know it’s from Google.”
By becoming creative and adding more in-depth value to the content you create, you can place your website in a strong position. SEO is all about adaptability. Google is sure to focus on its users’ stickiness as you care for your visitors’ stickiness on your website. Let the smart play game begin!